Zero Trust Security Architecture – Explained Simply
We use email, online storage, and video calls every day.
That is why a new idea called Zero Trust Security Architecture is becoming popular. It means we do not trust anyone automatically—whether it is someone inside our company or outside. We check them first, and only then give access.
Let’s break this down in plain, friendly English—just like telling a friend.
What Is Zero Trust?
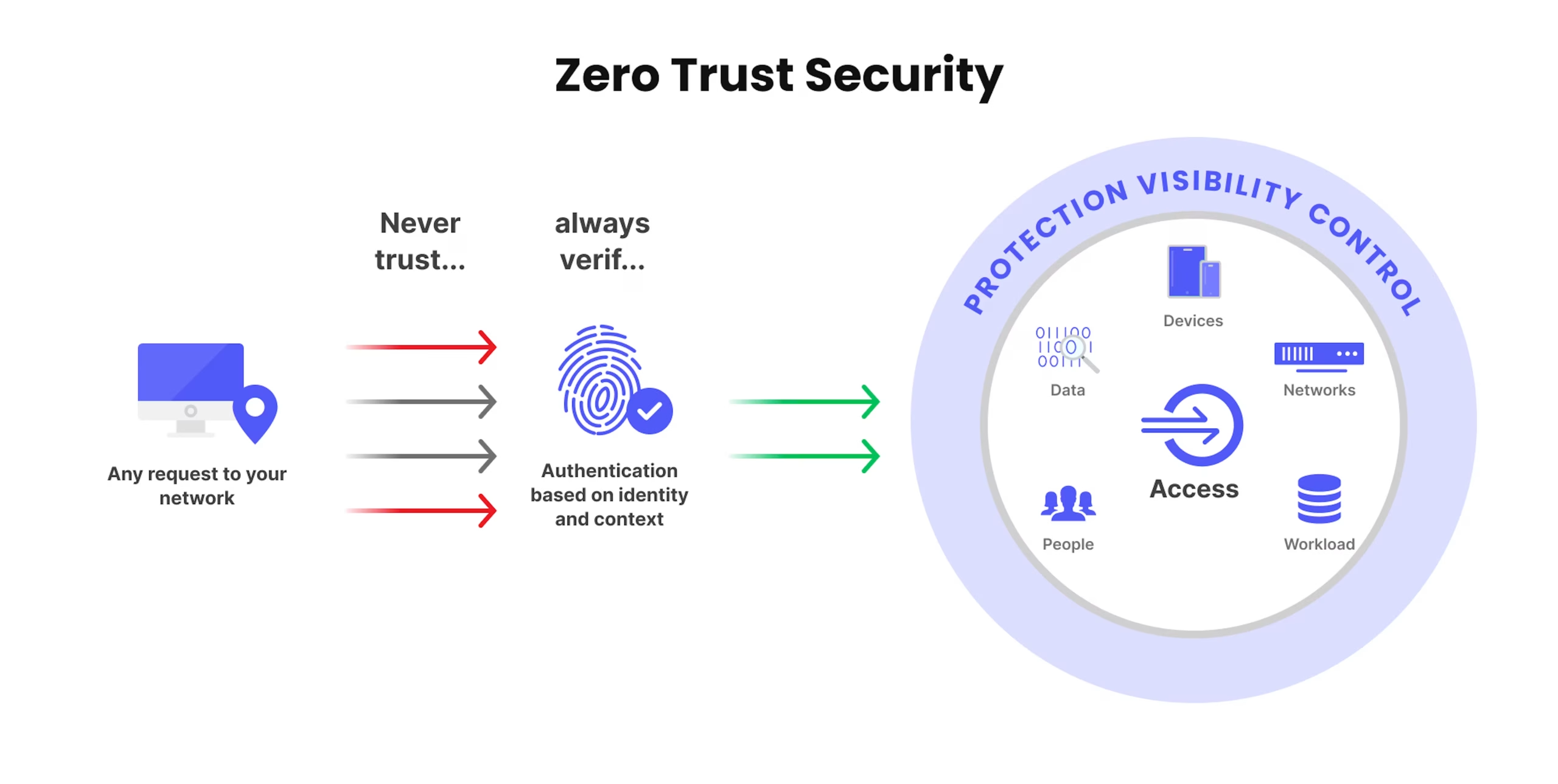
Think of your home with the door always open—anyone can walk in. Zero Trust is like locking that door with a rule: “Show your ID before you enter.”
In computer systems, Zero Trust says: Do not trust any request—no matter where it comes from. Always check ID and context first.
How Is This Different from Old Security?
Old systems let anyone inside the company network use everything. That sounds easy, but it is dangerous—if hackers get in once, they can see and take everything.
Zero Trust is the opposite. Every request is checked, every time. This reduces breaches and keeps data safer.
Simple Steps in Zero Trust
Verify Everything
Every user, device, and request must be checked first.
Least Access Only
Give people only what they need—nothing more.
Divide Network Into Parts
Break your system into smaller secure zones. If one is attacked, the rest stay safe.
Always Watch for Weird Behaviour
Keep an eye on everything. If something odd shows up, act quickly.
Auto-Respond to Threats
If something looks wrong, the system itself should respond—like cutting off access or sending an alert.
Here is an Example
Before, anyone on the office network could access anything—if a hacker got in, it was full access.
But with Zero Trust, it is different. The system checks: Is this person real? Is the device safe? Is what they want to do okay? Only after verifying, does it grant access.
Why Zero Trust Helps
What Zero Trust Protects
Keeps Data Safe: Only people who are allowed can see important info.
Stop Bad Actions from Inside: Even if someone is inside, they can’t do bad things without permission.
Helps People Work from Anywhere Safely: Every time someone tries to use the system, they are checked.
Harder for Hackers to Break In: Hackers have fewer chances to cause problems.
Problems with Zero Trust
Zero Trust is good, but not easy:
Needs Changes: Companies must change how things work.
Can Be Slower: People have to wait for checks each time they use the system.
People Must Learn New Rules: Everyone needs to know how to use the new system.
Needs New Tools: Companies need special programs to check users and watch for problems.
Who Uses Zero Trust?
Banks: They protect money and important info.
Hospitals: They keep patient info very safe.
Tech Companies: Many workers use the internet, so every login is checked.
Zero Trust helps keep data safe and stops bad people from causing harm.
Simple Comparison: Old Security vs Zero Trust
In old security systems, anyone inside the network was trusted automatically. In old systems, if a hacker got in once, they could see everything. But Zero Trust checks every step, so one mistake won’t give full access. Working from home used to be unsafe, but Zero Trust keeps it safe by checking each connection. Old systems had weak spots, but Zero Trust uses many ways to keep data safe.
Final Thoughts
With Zero Trust:
Every user and device is verified
People get only what they need
Breaches do not spread easily
Remote and office environments stay secure
Zero Trust is a modern, strong way to handle security in today’s digital world.